Newly-released ELISA pack for Kynurenic / Quinolinic Acids
Through the degradation of L-Tryptophan, the Kynurenine pathway (KP) generates a series of catabolites collectively known as Kynurenines, which can exert immunomodulatory and/or neuroactive properties. Known to respectively harbor neuroprotective and neurotoxic functions, Kynurenic (KYNA) and Quinolinic (QA) acids are found to be dysregulated in several neuroinflammatory disorders including Parkinson and Alzheimer disease but also Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Multiple Sclerosis. Manipulating the Kynurenine Monoamine Oxygenase (KMO) – an enzyme at the crossroads of KYNA and QA – has been proposed as a valuable therapeutic approach to shift Kynurenine degradation towards the formation of KYNA.
We developed novel ELISA detection kits to monitor the imbalance between KYNA and QA levels in neurological diseases and evaluate the ability of novel KMO inhibitors to restore equilibrium within the KP and mitigate neurodegeneration.
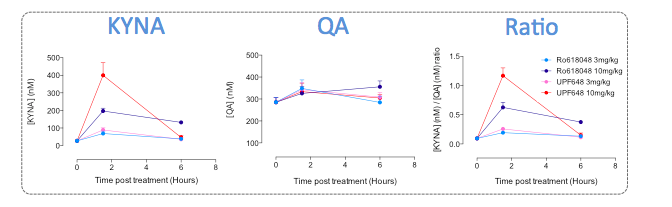
Measurement of plasma levels of both KYNA and QA in mice treated with KMO inhibitors. Mice were treated with two selective KMO inhibitors – Ro-618048 & UPF648 – at two different doses each. Plasma samples were collected before treatment and at 1h30 and 6h post-treatment. KYNA and QA levels were then quantified by mean of ELISA (IS-I-0200 and IS-I-0100). As depicted above, blockade of KMO time- and dose-dependently favors the degradation of Kynurenine into KYNA. Interestingly, no major effect is observed on QA level thus suggesting compensatory mechanism to maintain stable circulating QA level.