No products in the cart.
Xanthurenic acid Antibody – Rabbit Polyclonal
Ref: IS1014IFIHCKynurenine pathwayTryptophan metabolismPolyclonal AntibodiesICC
 +
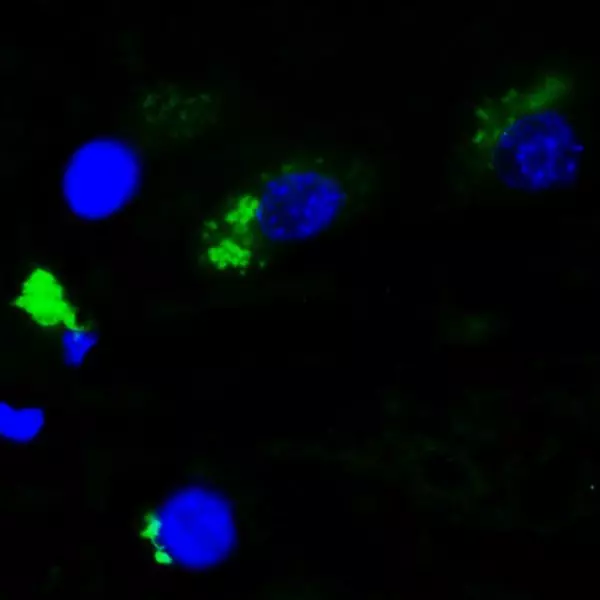
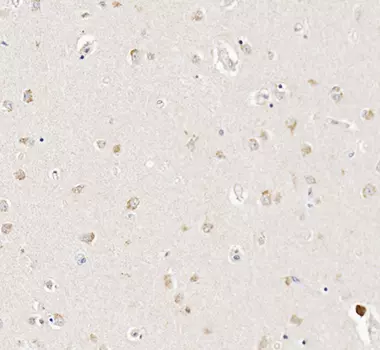
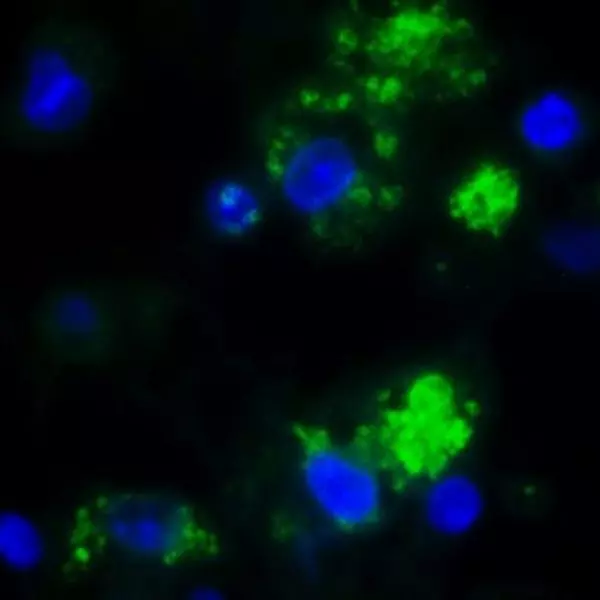
+Xanthurenic acid in mouse brain tissue sections
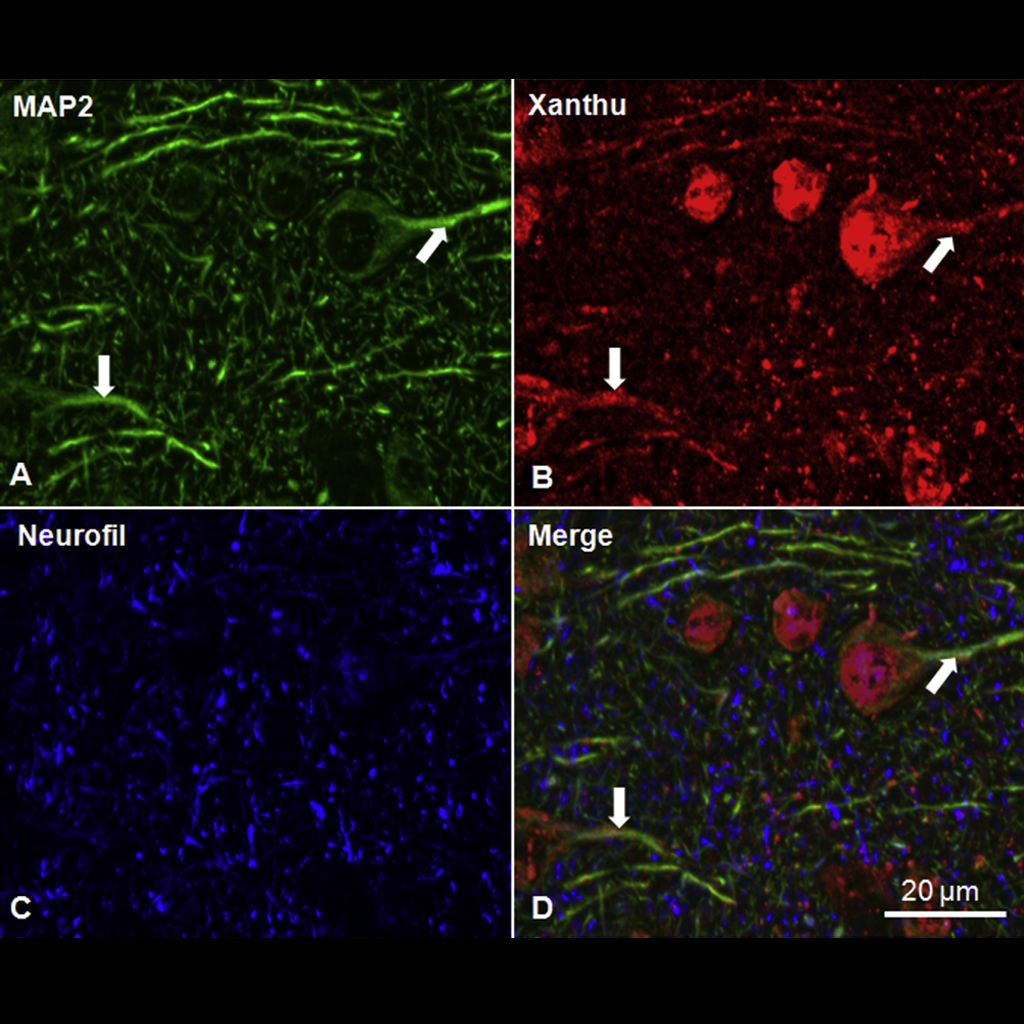
Published by Roussel et al., in 2016. Staining in mouse cortical tissues sections evidences the presence of Xanthurenic acid in cortical neurons (bodies and dendrites), and its absence from axons.
DatasheetMSDS
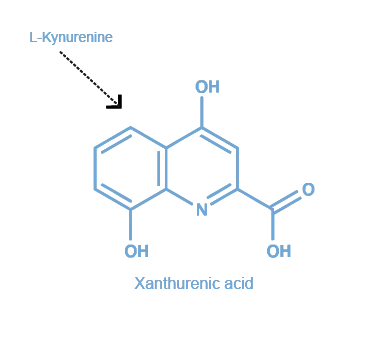
IS1014 was the first anti-Xanthurenic acid cited in the literature, by Roussel et al., in 2016. In this paper, this highly affine rabbit pAb was used to label Xanthurenic acid in mouse brain tissue sections and rat primary neurons.
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Host | Rabbit (see anti-XA mouse mAb) |
| Applications | IHC / IF |
| Reactivity | Reacts with all species |
| Format | 50µL |
| Reference | Roussel et al, Neuroscience, 2016 |
| Size | 50µg |
|---|
440.00€
99 in stock
Worldwide shipping
Product overview
| Product name | Xanthurenic acid polyclonal antibody |
| Synonyms | Anti-Xanthurenic acid polyclonal antibody 8-Hydroxy-4-oxo-1H-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid polyclonal antibody Xanthuric acid polyclonal antibody Xanthurenate polyclonal antibody 8-Hydroxykynurenic acid polyclonal antibody |
| Immunogen | Conjugated Xanthurenic acid |
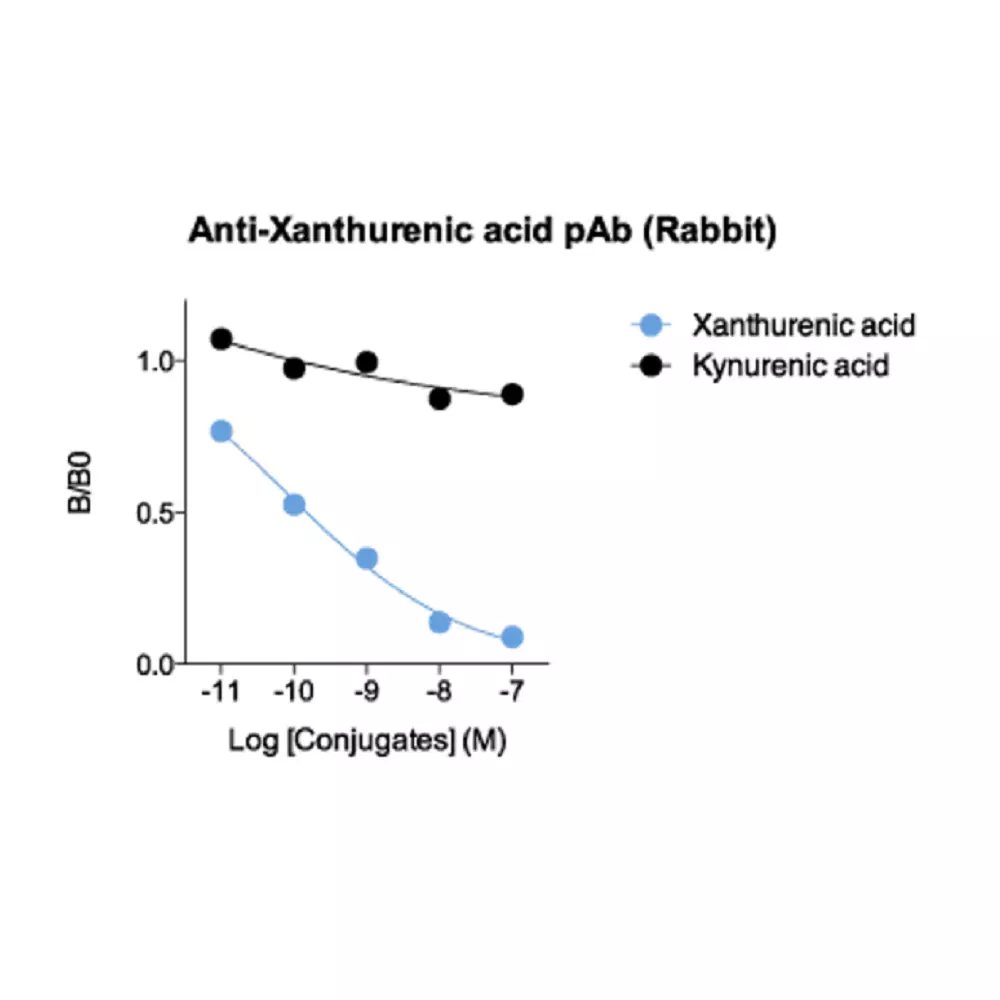
| Specificity | When tested in competitive ELISA, the anti-conjugated Xanthurenic acid antibody did not display any significant cross-reactivity with analog Kynurenic acid conjugate |
Reconstitution & storage
| Form | Liquid |
| Purity | Purified anti-serum |
| Storage | Store at 4°C |
| Storage buffer | Before use, vial should be resuspended in 50 µL of ultrapure water. Store at +4°C for short term (1-2 months). Aliquot and store at -20°C for long term. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles |
| Material safety datasheet | Download MSDS |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Optimal working conditions must be determined by the end-user |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | Optimal working conditions must be determined by the end-user |
| Restrictions | For research use only |
Product citation
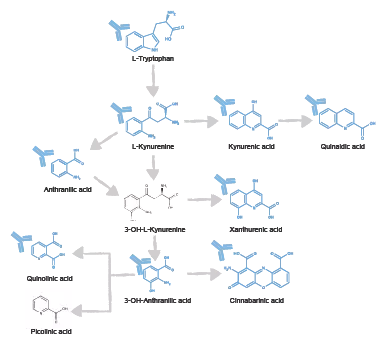
- Xanthurenic acid is localized in neurons in the central nervous system
Check the article
Authors : Roussel et al., Neuroscience
2016-05